Surgical removal of the gallbladder called cholecystectomy nowadays done laparoscopically is the time honoured, safest and definitive treatment of gallstone disease.
Stones in the gallbladder affect about 10-20 percent of the Indian population. It is one of the most common problems for which patients undergo surgery.
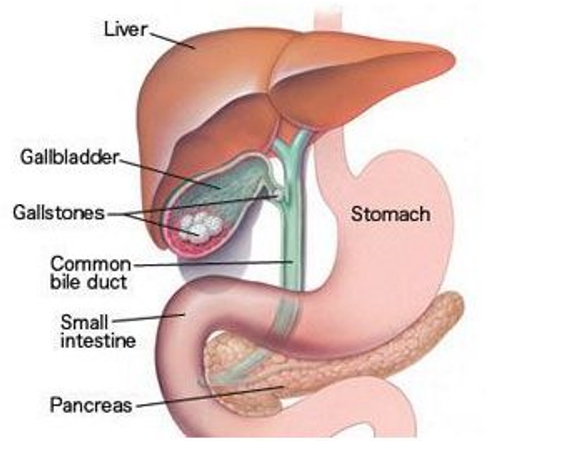
THE GALLBLADDER AND GALLSTONES
The gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ that rests beneath the right side of the liver. Bile is present in it and is stored in the gallbladder.
Gallstones are hardened deposits of bile, consisting mainly of cholesterol and bile salts that form in the gallbladder.
SYMPTOMS
• Not all gallstones produce symptoms.
• mild to severe abdominal pain especially in the upper part of the abdomen.
• indigestion or heartburn.
• nausea and vomiting.
DIAGNOSIS
• Ultrasonography of the whole abdomen is the investigation of choice.
• If you have jaundice MRI will be required to see if the stones have entered the bile duct.
COMPLICATIONS
• It can cause inflammation of the gallbladder a condition called as Acute cholecystitis.
• There can be blockage of the common bile duct which can lead to jaundice & bile duct infection.
• It can also cause inflammation of the pancreas. This condition is called Pancreatitis.
MYTHS
• Gallbladder removal will hamper digestion.
• Gallstones are only removed and not the gallbladder.
• The answer to these is that the Gallbladder is removed totally along with the stones. The gallbladder does not make bile, it only stores it. So once the gallbladder is removed the bile is still released continuously in the body to help in digestion.
TREATMENT:
Surgical removal of the gallbladder called cholecystectomy nowadays performed through key-hole surgery called laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the time honoured, safest and definitive treatment of gallstone disease. It is performed by making small holes in the abdomen and the gallbladder along with the stones are removed. Medical treatment to treat gallstone disease has been largely unsuccessful at this stage.
POST-SURGERY:
Most patients go home within 24hrs. Walking is encouraged and the patients can return to normal activity within 5-7 days. Avoid a high-fat diet for a week. Following that normal diet can be resumed.
